Individual results may vary
”The reason I stay on GIVLAARI is
because with fewer attacks, I feel like
I have more control back in my life.
I’m able to make plans for the future.”
—Amalia, an artist and Alnylam Patient Ambassador on GIVLAARI

Individual results may vary
”The reason I stay on GIVLAARI is
because with fewer attacks, I feel like
I have more control back in my life.
I’m able to make plans for the future.”
—Amalia, an artist and Alnylam Patient Ambassador on GIVLAARI

GIVLAARI® (givosiran) study results
In a 6-month study, GIVLAARI reduced AHP attacks and days of hemin use compared with placebo
In the study, 48 patients received GIVLAARI and 46 patients received placebo (an injection that did not contain any medicine) once monthly over a 6-month period. During the study, patients were able to use hemin if they experienced an attack. Using hemin to prevent an attack was not allowed during the study.
Patients taking GIVLAARI experienced fewer AHP attacks on average compared with those taking a placebo

 Patients on GIVLAARI had an average of 1.9 AHP attacks compared with 6.5 in patients on placebo
Patients on GIVLAARI had an average of 1.9 AHP attacks compared with 6.5 in patients on placebo
Attacks were defined as those that required hospitalization, urgent healthcare visit, or intravenous (IV) hemin administration at home.
Patients taking GIVLAARI experienced fewer days of hemin use on average to treat AHP attacks compared with those taking a placebo

 Patients on GIVLAARI had an average of 4.7 days of hemin use compared with 12.8 in patients on placebo
Patients on GIVLAARI had an average of 4.7 days of hemin use compared with 12.8 in patients on placebo
Fewer patients experienced AHP attacks over 36 months
After the 6-month study, all 93 eligible patients who remained in the study received GIVLAARI once a month. The graph below shows the 48 patients who were treated with GIVLAARI in the 6-month study and continued on in the study. Over time, fewer patients had attacks.
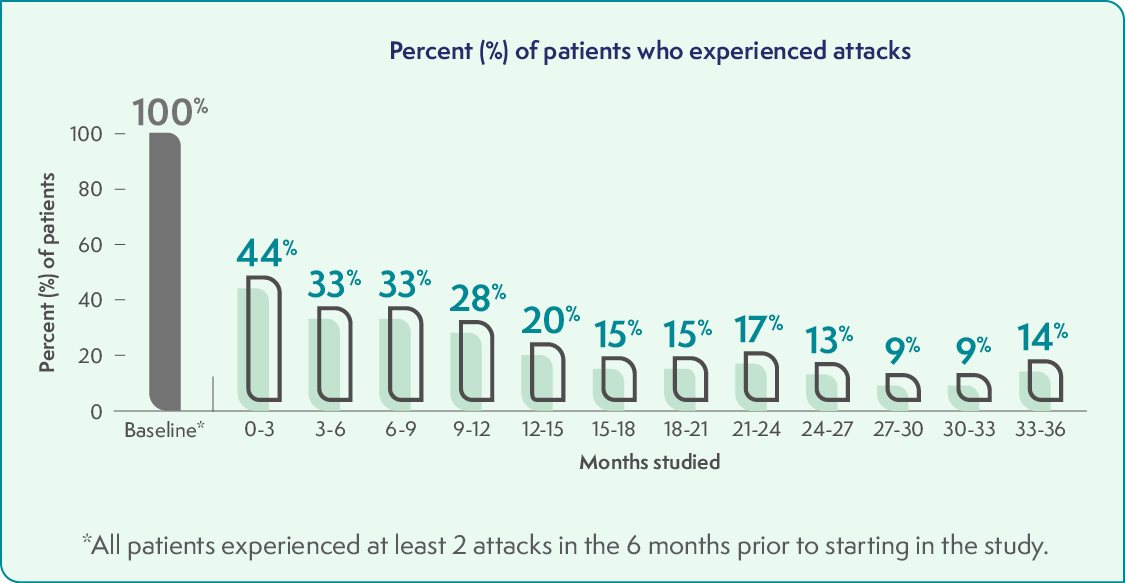
An attack during the study meant the patient needed hospitalization, an urgent healthcare visit, or intravenous (IV) hemin administration at home.
These results were observed in the clinical trial. Keep in mind that everyone responds to GIVLAARI differently.
GIVLAARI safety profile
Safety during the first 6 months of the study
- In the first 6 months of the study, 1 patient taking GIVLAARI stopped treatment due to changes in liver function. No patients taking placebo stopped treatment
The most common side effects in patients treated with GIVLAARI compared with those taking placebo in the first 6 months of the study were:
| GIVLAARI (48 patients) |
Placebo (46 patients) |
|
| Nausea | 27% | 11% |
| Injection site reactions | 25% | 0% |
| Rash | 17% | 4% |
| Changes in kidney function | 15% | 4% |
| Changes in liver function | 13% | 2% |
| Fatigue | 10% | 4% |
Safety through the 36-month study
- The most frequently reported adverse events occurring in ≥20% of patients were injection site reactions, nausea, fatigue, nasopharyngitis, headache, urinary tract infection, and upper respiratory tract infection
- Increased blood homocysteine was reported in 15 of 93 (16%) patients treated with GIVLAARI
